Newtons law & Propeller
What is Newtons
second law and how it matches with Aircraft Engine?
If
some mass ‘M” is accelerated, then a force presents. Same way the mass of fuel
air mixture is accelerated by a chemical reaction thus creates exhaust force.
What is Newtons third
law and how it matches with Aircraft Engine?
For
every action there is an equal but opposite reaction. The exhaust force created is also having
equal and opposite reaction called Thrust which is always in the direction of
flight.
What is a propeller?
And how it functions?
A
propeller is simply a rotating aerofoil. It provides thrust in the same way as
how an aerofoil mounted on wing generates lift. To know how a wing generates lift click here.When propeller rotates, the hub has
to cover a least circular path whereas the tip has to travel a large circular
path; in the same time. So propeller tip will be experiencing high speed than
hub; that means from hub to tip speed is increasing.
Suppose
if we want to have a uniform thrust all along the length of propeller, the
propeller must be designed by adding more aerofoil at various angle of
incidence (or pitch) by taking consideration of the speed at the part. This is
the reason for twisted propellers. The tip will have lowest angle of incidence
where as the hub will have largest angle of incidence.
What are the types of
propeller?
Fixed
pitch propeller- The pitch can’t be changed after design
Adjustable
pitch propeller- The pitch can be adjusted at ground with engines off.
Constant
speed propeller- The pitch can be adjusted during flight to maintain a constant
speed.



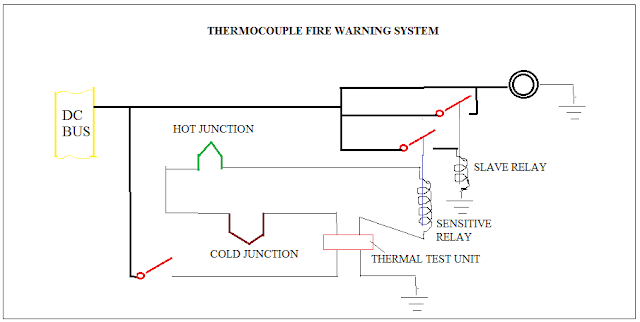
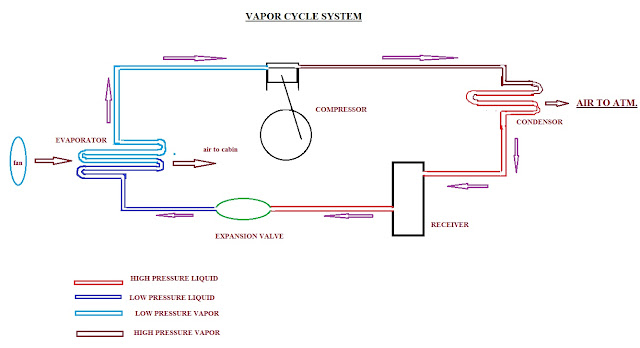
Comments
Post a Comment