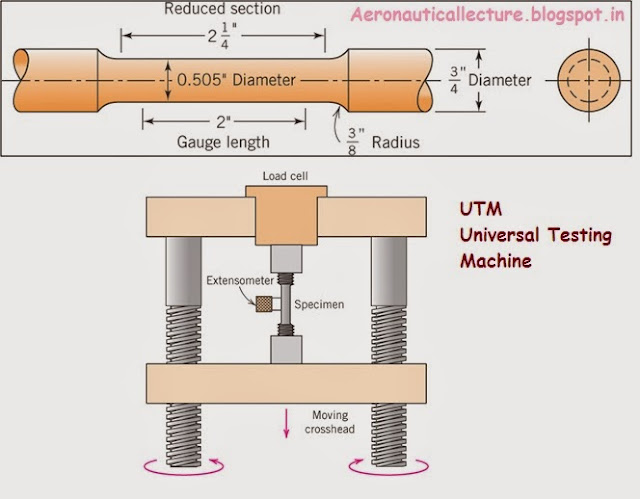
Stress strain Diagram part-2

Elastic Region (Point 1 –2) When we start to apply tensile pull on the specimen, the stress and strain develops,keeps on increasing in a proportional manner upto elastic limit. The material will return to its original shape after the material is unloaded (like a rubber band). The stress is linearly proportional to the strain in this region. Point 2: Yield Strength: A point where permanent deformation occurs. (If it is passed, the material will no longer return to its original length.) Tensile Strength (Point 3) The largest value of stress on the diagram is called Tensile Strength (TS) or Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS). It is the maximum stress which the material can support without breaking. Point 4: Strain Hardening If the material is loaded again from Point 4, the curve will follow back to Point 3 with the same Elastic Modulus (slope). The material now has higher yield strength of Point 4. Raising the yield strength by p...