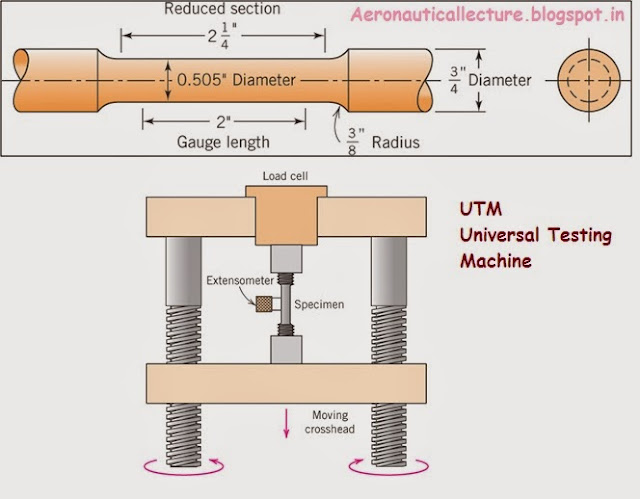
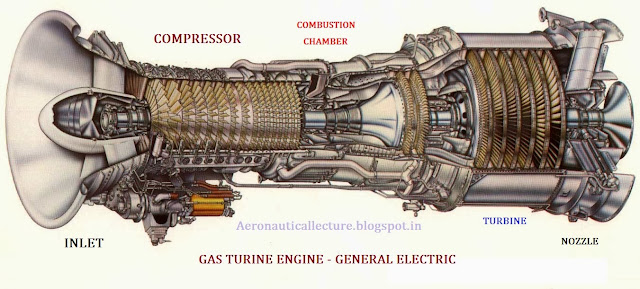
Continuum- Boundary layer- No slip condition

What is fluid mechanics? It is a science that deals with movement of fluids (Liquids/gas) and its interaction with solid surface. 99% of the practical flow is wall bounded. What is meant by continuum? All matters are made up of atoms, fluids too. Atoms have some gap in between them. Now just consider the flow over a circular cylinder of diameter d. The mean distance that an atom travels between two successive collisions is called as Mean free path (λ). When comparing λ and d, if λ is too small than d, we can assume that the flow over the cylinder as continuum. What is no- slip condition? Consider a fluid flow over a solid surface. The layer of fluid which is attached to the solid surface sticks to the solid surface and so it has zero relative velocity with the solid surface. This is what called as no-slip condition. Due to no slip phenomenon the layer of fluid attached with the surface has zero relative velocity and the next layers are moving with ...