Torque- Moment- Moment of inertia
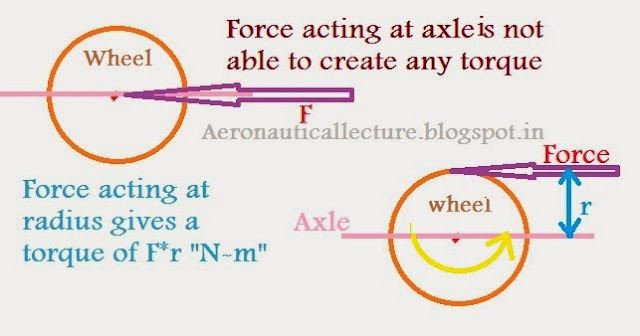
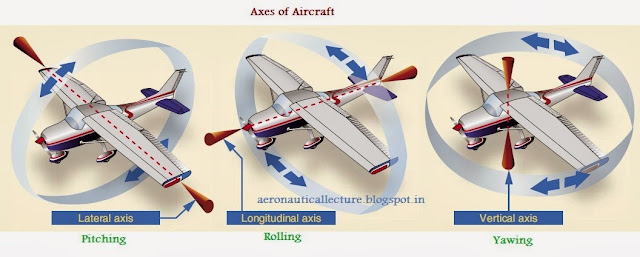
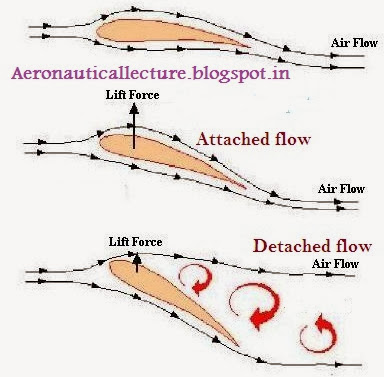
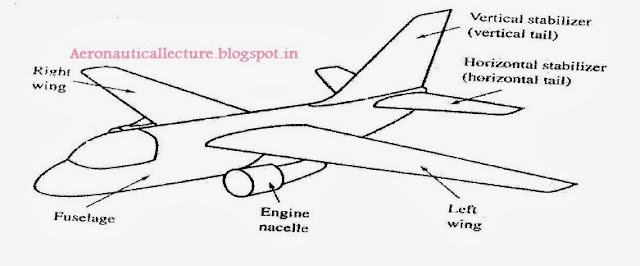
What is torque? Define moment? Torque is simply a moment of force. Moment of force is just the product of force and perpendicular distance. Unit “Nm”. What is Moment of Inertia? The moment of inertia measures the resistance to a change in rotation. Change in rotation comes from torque. Moment of inertia I = mr 2 . Please note moment of inertia strictly depends upon the axis of rotation.